Incoterms include standardized international commercial terms, recognized and used by many countries and territories. The content of Incoterm is related to two key points:
-
Responsibility between seller and buyer
-
The position transfers responsibility, risks, and costs from the seller to the buyer
Incoterms will be issued by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC). This Code is published in many languages and is most commonly used in English. Besides, you can also refer to Incoterm 2000, 2010, 2020 in Vietnamese from the publishing unit in Vietnam.
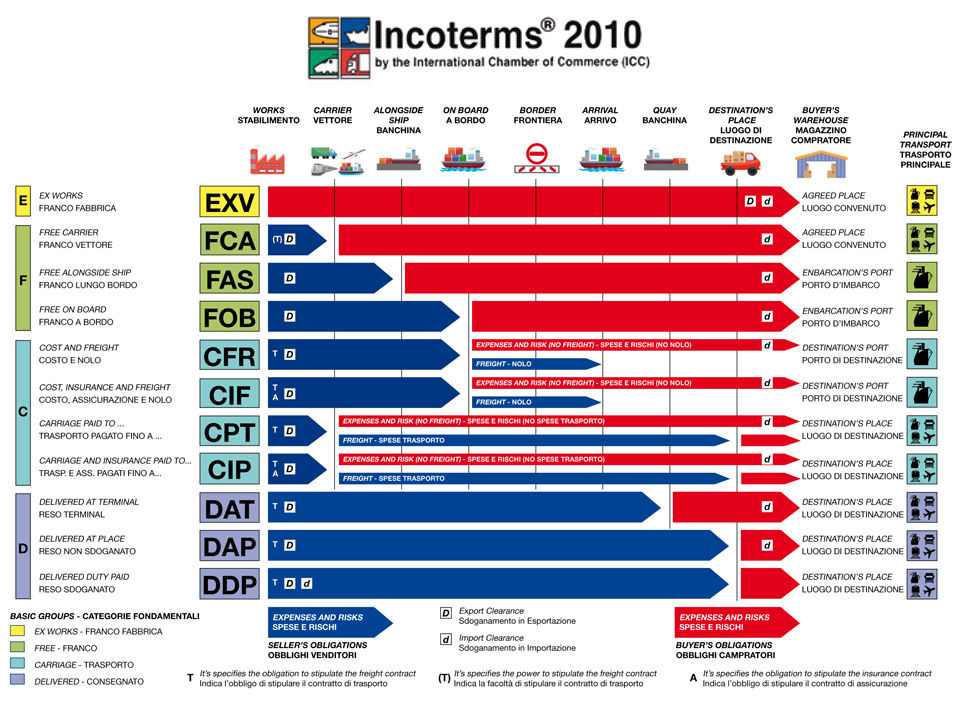
In Incoterm 2010, Incoterm is divided into 11 articles, located in 4 groups E, F, C, D, specifically as follows:
-
Group E: ExW (ExWork) factory delivery
-
Group F: FOB (Free On Board), FCA (Free Carrier), FAS (Free Alongside)
-
Group C: CRF (Cost & Freight), CIF (Cost Insurance & Freight), CPT (Carriage Paid To), CIP (Cost Insurance Paid To)
-
Group D: DAT (Delivered at Terminal), DAP (Delivered at Place), DDP (Delivered Duty Paid)
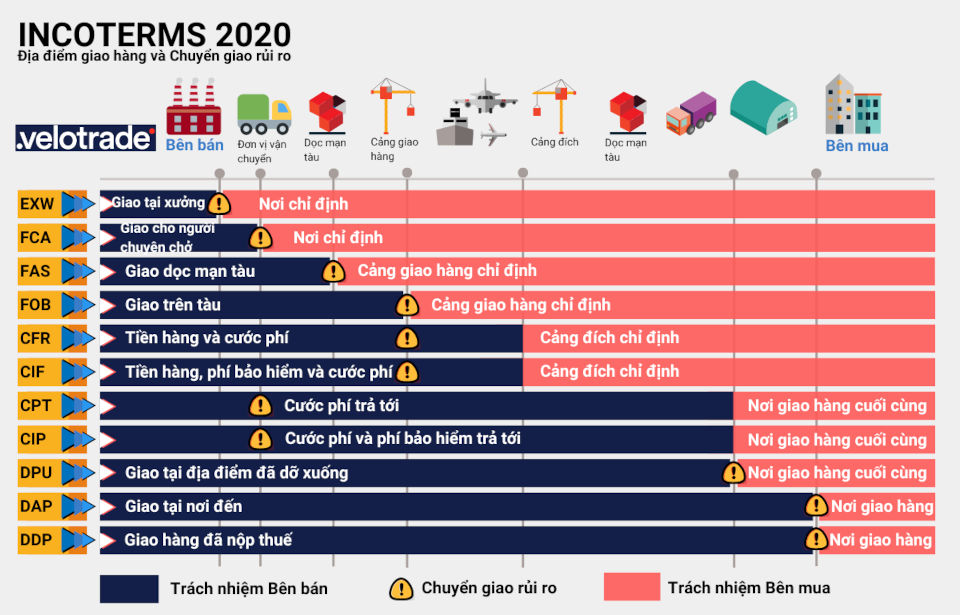
What is the difference between the 2020 and 2010 versions of Incoterm:
-
Specific explanation of Incoterm in the introduction
-
Add DPU condition (replacement for DAT)
-
Add regulations on Onboard bill of lading in FCA terms
-
Arrange the obligations of each party, clarify the content of delivery obligations and divide risks
-
The cost division regulations have been changed and moved to section A9/B9
Purpose: Incoterm was introduced to clarify international trade conditions. Thereby, dividing responsibilities, risks, and costs during the process of transferring goods from the seller to the buyer. Thanks to Incoterms, the parties involved in the transaction can reach an agreement. At the same time, minimize disputes arising due to disagreements and misunderstandings about rights and duties.
In the absence of Incoterms, the participating parties will have to negotiate and agree on every detail, leading to extended negotiation time, and the contract will also become lengthy and without focus. Instead, Incoterms provide a set of rules with attached conditions. Once you have chosen any terms, you will be considered to have agreed to those attached conditions.
WHAT ARE THE POINTS TO NOTE ABOUT INCOTERM?
Not mandatory
When participating in a signing, you need to note what is the role of Incoterm? First, Incoterms are not laws, so they are not mandatory. Incoterm is a commercial practice applied by many parties. So you can use the rules in Incoterm for reference. Only when both the seller and the buyer agree to certain conditions in the Incoterm. Then put it into the signing document. At this time, the content of Incoterm is applied and binding.
Many current versions
In fact, Incoterm has many versions and later versions do not negate the validity of previous versions. Incoterm versions issued in: 1936, 1953 (Revised in 1967 & 1976), 1980, 1990, 2000, 2010 and 2020. This requires that when using Incoterm in international trade, you need to clearly understand what the rules of each version of Incoterm are. From there, we can compare and determine the tasks and interests of the parties.
Only involved in locating risky moves
Incoterms are used to determine the transfer of responsibility, risk, and costs between seller and buyer. Other contents related to ownership of goods and remedies for breach of contract are not included. Therefore, these issues should be clearly agreed upon in the contract.




